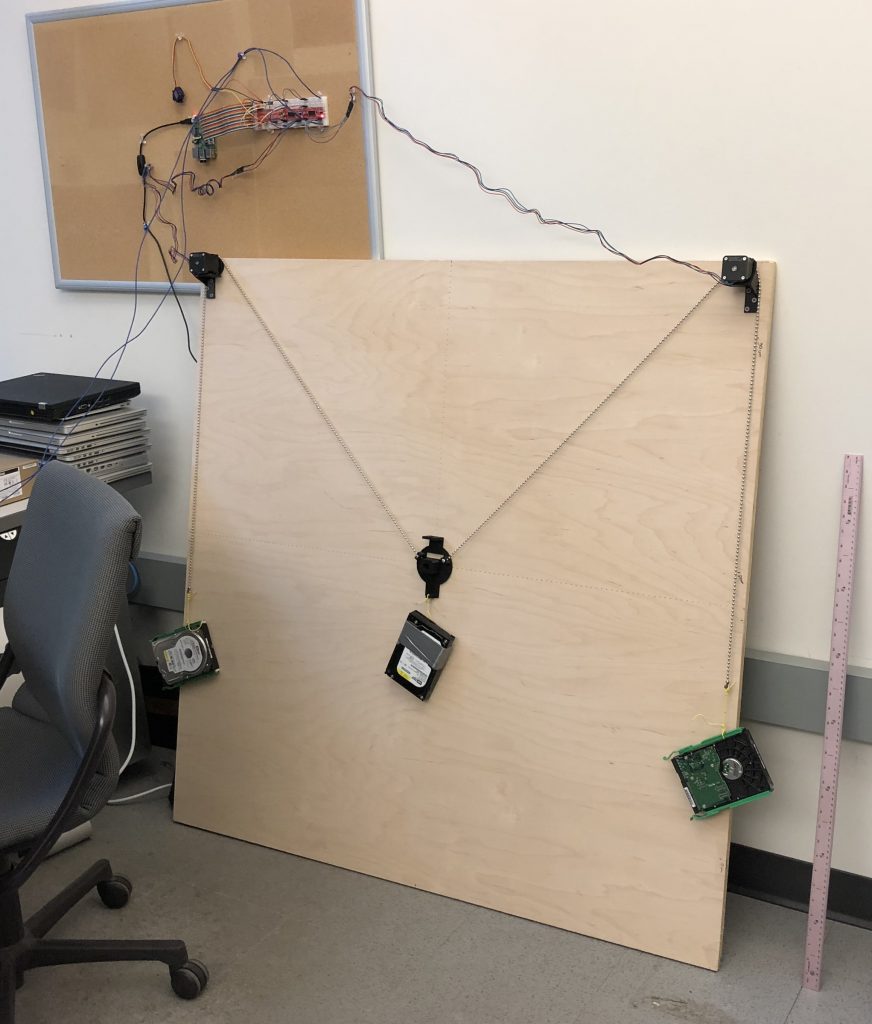
I lost a voltage sensor the exact minute thunder struck very close to the house, Nicole happened to be filming because it was an impressive mix of rain, hail & thunder. Does thunder create some sort of EMP? Could be a coincidence but the timing is really suspicious. Sorry I mean sus.
dead sensor :\
Oh, well I’ll just buy a replacement.
And fuck, I forgot we screw over allies and suck up to dictators now. Phidgets come from Canada, I never found any comparable alternatives in the realm of current sensing that goes beyond small hobbyist projects. And I don’t really want to relearn/recode a whole new deal anyway. I just want replacement parts.
Extensive searching pointed to robotshop.com having Phidgets parts in stock. So I grabbed spares for everything to get a few thunderstrikes ahead and buy me a few years. For the top 3 parts, I grabbed everything they are left.
The battery voltage sensor is actually important these days as automation uses it to make decisions on which circuits to turn on/off. So for a few days until I got the part, I moved the panels’ voltage sensor to the battery. Sensing the panels is informational and has no real consequence on function. With anything solar, I have appreciated having spares at hand so it was time to spend some money and make that true for the monitoring side of things which we became more dependent on over time.